
WIPO China: Global Innovation Index 2023— Switzerland, Sweden and the U.S. Lead the Global Innovation Ranking; Innovation Robust but Startup Funding Increasingly Uncertain

图:WIPO|Photo: WIPO
根据产权组织全球创新指数(GII),瑞士、瑞典、美利坚合众国、联合王国和新加坡是 2023年全球最具创新力的经济体,而一批中等收入经济体成为过去十年来排名上升最快的国家。
Switzerland, Sweden, the United States, the United Kingdom and Singapore are the world’s most innovative economies in 2023, according to WIPO’s Global Innovation Index (GII), as a group of middle-income economies have emerged over the past decade as the fastest climbers of the ranking.
2023年GII使用80个指标跟踪130多个经济体的全球创新趋势,为决策者和商界领袖激发人类才智提供指导。今年,该报告的结论是在2019冠状病毒病大流行后经济复苏迟缓,利率居高不下,地缘政治冲突持续的背景下发布的。
The GII 2023 uses 80 indicators to track global innovation trends in 130-plus economies, guiding policy makers and business leaders in stimulating human ingenuity. This year, the report‘s findings are unveiled against a background of slow economic recovery from the COVID-19 pandemic, high interest rates and geopolitical conflict.
2023版报告指出,有助于将人类才智转化为新产品和新服务的风险资本较去年大幅下滑,前景愈加不明。
The 2023 edition identifies an increasingly uncertain outlook for the venture capital (VC) that helps transform human ingenuity into new products and services, with the global value of VC funding marking a significant plunge last year.
在年度排名中,中国——GII前30名中唯一的中等收入经济体——排名第12位,日本紧随其后,排名十三。以色列(第14位)上升两名,重返15强。芬兰(第6位)、丹麦(第9位)、瑞典(第2位)和波罗的海经济体(爱沙尼亚第16位,立陶宛第34位,拉脱维亚第37位)均呈上升态势。
In the annual ranking, China – the only middle-income economy in the GII top 30 – ranks 12th followed by Japan in the 13th position. Israel (14th) is back among the GII top 15, gaining two steps. Finland (6th) is on an upward trend along with Denmark (9th), Sweden (2nd) and the Baltic economies (Estonia 16th, Lithuania 34th and Latvia 37th).
过去10年来,印度尼西亚(第61位)与中国、土耳其(第39位)、印度(第40位)、越南 (第46位)、菲律宾(第56位)和伊朗伊斯兰共和国(第62位)一道,成为GII排行榜上攀升最快的中等收入经济体。在过去的四年中,自大流行病开始以来,毛里求斯(第57位)、印度尼西亚、沙特阿拉伯、巴西和巴基斯坦的排名上升最快(按排名升幅排序)。
In the past 10 years, Indonesia (61st) joins China, Türkiye (39th), India (40th), Viet Nam (46th), the Philippines (56th), and the Islamic Republic of Iran (62nd) in the group of middle-income economies to have climbed the GII rankings fastest. In the last four years, and since the pandemic started, Mauritius (57th), Indonesia, Saudi Arabia, Brazil and Pakistan have risen the most in rank (in order of rank progression).
与发展水平相比,共有21个经济体的创新表现超出预期,其中大多数位于撒哈拉以南非洲和东南亚、东亚及大洋洲。印度、摩尔多瓦共和国和越南均连续13年在创新方面的表现超出预期。印度尼西亚、巴基斯坦和乌兹别克斯坦连续第二年、巴西连续第三年创新超出预期。
A total of 21 economies outperformed on innovation as expected relative to their level of development, the majority located in Sub-Saharan Africa and South East Asia, East Asia, and Oceania. India, the Republic of Moldova and Viet Nam are each innovation overperformers for 13 years in a row. Indonesia, Pakistan and Uzbekistan maintain their overperformer status for a second year and Brazil for a third consecutive year.
“一些新兴经济体在全球创新指数中的排名不断攀升,这表明关注创新生态系统可以带来变化。在全球范围内,尽管风险资本资金出现下滑,但2023年全球创新指数会让我们放心,创新活动目前继续保持强劲势头,但应继续从数量转向质量。
有了全球创新指数,全世界的政策制定者将继续拥有丰富、可信的数据和信息来源,以制定有利于创新的政策,释放人民的创新潜能。”
——产权组织总干事邓鸿森
“A group of emerging economies are consistently climbing the GII ranks, showing how a focus on the innovation ecosystem can make a difference. Globally, despite a downturn in venture capital funding, the GII 2023 should reassure us that innovative activity currently continues to run strong but that innovative activity should continue to shift from quantity to quality.
With the GII, policymakers across the world continue to have a rich and trusted source of data and information to craft pro-innovation policies to unleash the innovative potential of their people.”
——WIPO Director General Daren Tang
GII的专题摘录显示,全球五大科技集群目前均位于东亚,东京-横滨是最大的科技集群,而中国成为集群数量最多的国家。
A special excerpt from the GII shows that the world’s five biggest science and technology (S&T) clusters are now located in East Asia, with China emerging as the country with the greatest number of clusters as Tokyo-Yokohama leads as the biggest S&T cluster.
“
GII 的主要结论包括:
Among the GII’s key findings:
• 科学出版物、研发、风险资本交易(不包括价值)和专利等的数量继续增加,达到前所未有的水平。然而,增长率低于2021年的超常增长。
• Scientific publications, research and development (R&D), the number of venture capital (VC) deals (but not their value) and patents continued to increase to higher than ever levels. However, growth rates were lower than the exceptional increases seen in 2021.
• 研发投入最大的企业在2022年的支出达1.1万亿美元,创历史新高。这些企业2022年的研发支出增长约7.4%,低于2021年的15%。
• In 2022, spending by corporations representing the largest investors in R&D reached USD 1.1 trillion in 2022 – a historic high. They increased their R&D spend by around 7.4 percent in 2022, down from 15 percent growth in 2021.
• 与近期人工智能的迅猛发展相呼应,信息和通信技术(信通技术)硬件领域的显卡和芯片制造商在2022年的研发增长最为显著,遥遥领先。在大流行病期间削减了研发支出的其他行业,如汽车、旅游和休闲,在2022年再次出现强劲投资。
• Mirroring the recent surge of artificial intelligence, the ICT hardware sectors saw graphic card and chipmakers in the lead with the most notable R&D growth in 2022. Other sectors which cut back R&D spending during the pandemic, such as automobiles and travel and leisure, invested strongly again in 2022.
• 根据初步数据,估计2022年全球政府研发预算有实际增长。日本和大韩民国大幅增加,德国增幅较小,弥补了其他经济体的削减。
• According to preliminary data, global government R&D budgets are estimated to have increased in real terms in 2022. Significant increases took place in Japan and the Republic of Korea, and smaller ones in Germany, making up for cuts in other economies.
• 2022年,风险资本投资总值从2021年的超高水平大幅下降了近40%,反映了风险融资环境的恶化。非洲是2022年唯一没有出现下降的地区。
• Reflecting a deteriorating climate for risk finance, the total value of VC investments declined sharply by close to 40 percent in 2022, albeit from unusually high levels in 2021. Africa was the only region not to see a decline in 2022.
• 2023年和2024年的风险资本前景尚不明朗,高利率可能会继续影响创新融资。
• The VC outlook for 2023 and 2024 is uncertain, with high interest rates likely to continue to impact the financing of innovation.
• 信息技术、卫生和能源领域的指标继续显示出进步——《2022年全球创新指数》中概述的数字时代和深度科学创新浪潮正在蓬勃发展。
• Indicators in the fields of information technology, health and energy continue to show progress – the Digital Age and Deep Science innovation waves outlined in GII 2022 are well underway.
• 总体而言,尽管电动汽车和癌症治疗等一些技术的普及率仍然较低,但技术的应用呈积极态势。
• Overall, technology adoption is developing positively even though penetration for some technologies, such as electric vehicles and cancer treatment, remains low.
“
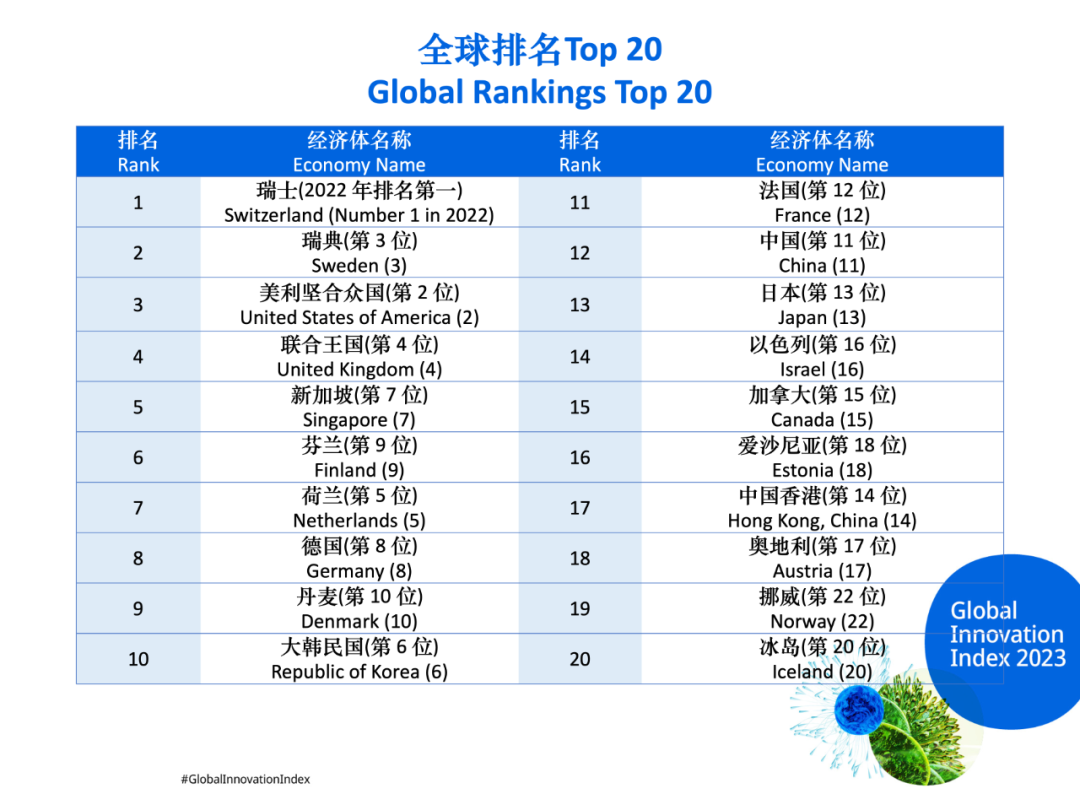
图:WIPO|Photo: WIPO
视频:2023年全球最具创新力经济体Top 10
Video: Top 10 Most Innovative Economies
视频:WIPO|Video: WIPO
GII联合编辑谈创新
GII Co-Editors on Innovation
“在许多国家的政府仍在为COVID期间积累的巨额公共债务而苦苦挣扎之际,企业界已在继续提高创新水平。然而,这一趋势可能掩盖了日益扩大的不平等,因为一些行业吸引了巨量资金(通常是人工智能),而融资链(尤其是针对小型企业和新兴企业的风险资本)却开始出现缺口。在贸易关系日趋紧张、国际合作水平下降的背景下,这种趋势可能会阻碍创新型公司为恢复可持续增长而做出充分贡献的能力。”
—— 欧洲工商管理学院(INSEAD)杰出研究员、GII联合编辑布吕诺·朗万
“While many governments still struggle with the massive amounts of public debt accumulated during COVID, the business sector has continued to increase its levels of innovation. However, this trend may hide growing disparities, as some sectors have attracted significant funding (typically artificial intelligence) while gaps have started to appear in the financing chain, especially venture capital for small and new businesses. Against the background of growing trade tensions and lower levels of international cooperation, such trends could hamper the ability of innovative firms to fully contribute to the resumption of sustainable growth.”
——INSEAD Distinguished Fellow and GII Co-Editor Bruno Lanvin
“我们正在见证数字技术和许多深度科学领域的指数级进步。这为各行各业的创新提供了动力,并有望为我们这个世界在气候、粮食、卫生和相关挑战方面的一些复杂问题提供解决方案。”
——GII联合编辑、牛津大学赛德商学院院长
苏米特拉·杜塔
“We are witnessing exponential progress in digital technologies and many fields of deep science. This is providing a boost to innovation across sectors and holds the hope of providing solutions to some of our world’s complex problems in climate, food, health and related challenges.”
——GII Co-editor and Dean of the Saïd Business School at Oxford University Soumitra Dutta
按地区分列的 2023 年全球创新领先者
Global leaders in innovation in 2023 – Regional Breakdown
“
北美洲
Northern America
在2023年GII的80项创新指标中,美利坚合众国(第3位)在13项指标上都在全球拔得头筹。它在全球企业研发投资者、接收的风险资本、高校质量、独角兽公司综合估值和企业无形资产价值密集度等多项关键指标上均位居世界第一。
The United States (3rd) scores the best in the world in 13 of the 80 GII 2023 innovation indicators. It holds the number one spot globally in various critical indicators, including global corporate R&D investors, VC received, university quality, combined valuation of unicorn companies and the value of corporate intangible asset intensity.
加拿大(第15位)仍然稳居全球创新15强之列。它在风险资本接收者(第1位)、科学出版物的影响力(H指数,第4位)和软件支出(第5位)等指标上排名第一。
Canada (15th) remains firmly positioned among the top 15 global innovators. The country leads in indicators including VC recipients (at first place), impact of its scientific publications (H-Index, 4) and software spending (5).
欧洲
Europe
在排名前25位的经济体中,欧洲拥有最多的创新领先者,共计16个,比2022年多一个。在39个上榜的欧洲经济体中,今年有19个(比去年多7个)提升了名次,分别是瑞典(第2位)、芬兰(第6位)、丹麦(第9位)、法国(第11位)、爱沙尼亚(第16位)、挪威 (第19位)、爱尔兰(第22位)、比利时(第23位)、意大利(第26位)、葡萄牙(第30位)、立陶宛(第34位)、拉脱维亚(第37位)、希腊(第42位)、斯洛伐克(第45位)、罗马尼亚(第47位)、塞尔维亚(第53位)、北马其顿(第54位)、乌克兰(第55位)和阿尔巴尼亚(第83位)。
Europe hosts the greatest number of innovation leaders among the top 25 – 16 in total, one more than in 2022. Out of 39 European economies covered, 19 move up the rankings this year (seven more than last year), namely Sweden (2nd), Finland (6th), Denmark (9th), France (11th), Estonia (16th), Norway (19th), Ireland (22nd), Belgium (23rd), Italy (26th), Portugal (30th), Lithuania (34th), Latvia (37th), Greece (42nd), Slovakia (45th), Romania (47th), Serbia (53rd), North Macedonia (54th), Ukraine (55th) and Albania (83rd).
在表现有所改善的经济体中,法国在无形资产(第3位)、全球品牌(第4位)、工业品外观设计(第8位)和全球企业研发投资者(第9位)方面表现出色。比利时在研发支出(第6位)、研究人员(第8位)和高校—产业研发合作(第9位)方面表现出色。
Among economies improving their performance, France excels in intangible assets (at third place), global brands (4), industrial designs (8) and global corporate R&D investors (9). Belgium performs well in R&D expenditure (6), researchers (8) and university- industry R&D collaboration (9).
塞尔维亚接近前50名,在外国直接投资流入量(第11位)和劳动生产率增长(第14位)方面表现突出。
Serbia approaches the top 50 with a strong performance in foreign direct investment (FDI) inflows (11) and labor productivity growth (14).
东南亚、东亚和大洋洲
South East Asia, East Asia, and Oceania
东南亚、东亚和大洋洲有六个经济体在创新方面处于世界领先地位,分别是新加坡(第5位)、大韩民国(第10位)、中国(第12位)、日本(第13位)、中国香港(第17位)和澳大利亚(第24位)。
Six South East Asia, East Asia and Oceania (SEAO) economies are world innovation leaders, namely Singapore (5th), the Republic of Korea (10th), China (12th), Japan (13th), Hong Kong, China (17th) and Australia (24th).
东南亚、东亚和大洋洲今年有八个经济体提升了名次,其中印度尼西亚(从第75位上升至第61位)的升幅最大。它在信通技术相关指标方面表现优异,在高校—产业研发合作(第5位)、集群发展情况(第5位)、创业政策和文化(第5位)以及初创企业和新创企业融资 (第8位)等方面跻身全球前十。它在创新产出方面取得了显著进步,尤其是在知识创造和在 线创意方面。
Eight economies within the SEAO region improve their rankings this year, with Indonesia (61st, up from 75th) making the greatest advance. Indonesia excels in ICT- related indicators and ranks among the top 10 globally for university-industry R&D collaboration (5), state of cluster development (5), entrepreneurship policies and culture (5) and finance for startups and scaleups (8). Indonesia has made marked improvements in innovation outputs, notably in knowledge creation and online creativity.
蒙古(第68位)、文莱达鲁萨兰国(第87位)和老挝人民民主共和国(第110位)的排名也有所上升。
Mongolia (68th), Brunei Darussalam (87th) and the Lao People’s Democratic Republic (110th) also move up the rankings.
中亚和南亚
Central and Southern Asia
在中亚和南亚,印度(第40位)是该地区排名最靠前的创新经济体。伊朗伊斯兰共和国(第62位)、哈萨克斯坦(第81位,该地区前三名的新晋成员)和乌兹别克斯坦(第82位)接近前80名。
In Central and Southern Asia, India (40th) is the best-ranked innovation economy in this region. The Islamic Republic of Iran (62nd), Kazakhstan (81st), and a newcomer in the regional top three), and Uzbekistan (82nd) get close to the top 80.
印度总排名保持在第40位,并在中等偏下收入国家中拔得头筹。它保持了连续13年在创新方面表现超出预期的记录,并在信通技术服务出口(第5位)、接收的风险资本(第6位)、科学和工程专业毕业生(第11位)和全球企业研发投资者(第13位)等关键指标上名列前茅。
India maintains its 40th position overall and takes the helm in the lower middle-income group. It holds the record for overperforming on innovation for the 13th consecutive year. India holds top rankings in key indicators including ICT services exports (at place 5), VC received (6), graduates in science and engineering (11) and global corporate R&D investors (13).
伊朗伊斯兰共和国保住了该地区第二的席位。它在商标(第1位)方面全球第一,在无形资产 (第13位)方面表现出色,在科学和工程专业毕业生(第3位)、市场资本化(第5位)和 工业品外观设计(第11位)等指标上均进入全球15强。
The Islamic Republic of Iran secures the 2nd position within the region. It claims the top spot globally in trademarks (at first place), performs well in intangible assets (13), and is in the top 15 worldwide in graduates in science and engineering (3), market capitalization (5) and industrial designs (11).
哈萨克斯坦新晋级地区三强,与尼泊尔(第108位)一起成为该地区仅有的排名上升的两个经济体。巴基斯坦和乌兹别克斯坦连续第二年在创新方面表现出色,巴基斯坦也是过去四年在GII上升最快的经济体之一。
Kazakhstan emerges as a newcomer in the regional top three and is one of only two economies that go up the rankings in the region, together with Nepal (108th). Pakistan and Uzbekistan overperform on innovation for the second consecutive year, while Pakistan also positions itself among the economies that have shown the most significant ascent in the GII over the past four years.
北非和西亚
Northern Africa and Western Asia
以色列(第14位)、塞浦路斯(第28位)、阿拉伯联合酋长国(第32位)和土耳其在该地区的创新排名中名列前茅。
Israel (14th), Cyprus (28th), the United Arab Emirates (32nd) and Türkiye lead in the innovation rankings for this region.
以色列排名上升两位,在九项创新指标上领先世界,包括研发支出、高校—产业研发合作、独角兽公司累计估值、产权组织《专利合作条约》(PCT)专利申请以及信通技术服务出口。
Israel gained two ranks. It leads the world in nine innovation indicators, including R&D expenditure, university-industry R&D collaboration, the cumulative value of its unicorn companies, WIPO Patent Cooperation Treaty (PCT) patent applications and ICT services exports.
阿拉伯联合酋长国稳定在前30名左右,在创业政策和文化、经商政策、企业研究人员数量以 及私营部门供资的研发方面排名前五。土耳其仍稳居GII排名前65位的中等收入经济体之列,在过去十年中排名上升最快。它在产业多样化方面排名前五,在无形资产、工业品外观设计和商标申请量方面表现尤为突出。
The United Arab Emirates stabilizes close to the top 30 and ranks in the top five for its entrepreneurship policies and culture, policies for doing business, the number of researchers in businesses, and R&D financed by the private sector. Türkiye remains firmly placed among the group of middle-income economies within the GII top 65, and has climbed fastest in the ranks over the last decade. It ranks in the top five for its industry diversification, and excels notably in intangible assets, industrial designs and trademark filings.
沙特阿拉伯(第48位)和卡塔尔(第50位)进入前50名。沙特阿拉伯在信通技术普及率 (第7位)、信通技术使用率(第10位)和经商政策(第16位)方面表现出色。此外,沙特阿拉伯在全球企业研发投资者(第16位)和全球品牌价值(第18位)方面也表现优异。
Joining the top 50 ranks are Saudi Arabia (48th) and Qatar (50th). Saudi Arabia performs well in ICT access (7), ICT use (10) and policies for doing business (16). Additionally, it excels in global corporate R&D investors (16) and global brand value (18).
巴林(第67位)、阿曼(第69位)、约旦(第71位)和埃及(第86位)等经济体的创新排 名也有显著提高。巴林和阿曼都进入前70名,而阿曼则在科学和工程专业毕业生(第2位) 和学生人均政府支出(第9位)方面跻身全球十强。
The economies of Bahrain (67th), Oman (69th), Jordan (71st) and Egypt (86th) also experience significant improvements in their innovation rankings. Bahrain and Oman both enter the top 70, while Oman secures a spot among the top 10 worldwide in graduates in science and engineering (2) and government funding per pupil (9).
格鲁吉亚(第65位)和亚美尼亚(第72位)也取得明显进步。
Georgia (65th) and Armenia (72nd) also make notable improvements.
拉丁美洲和加勒比
Latin America and the Caribbean
在拉丁美洲和加勒比地区,巴西于2023年跻身50强经济体之列。经过近几年的稳步上升,巴西首次超过智利(第52位),成为该地区最具创新力的经济体。墨西哥(第58位)紧随其后,保持了地区第三。
In Latin America and the Caribbean, Brazil breaks into the top 50 economies in 2023. Following a steady ascent in recent years, it surpasses Chile (52nd) for the first time, securing its position as the most innovative economy in the region. Mexico (58th) follows, holding the third regional position.
巴西今年的排名上升了五位,成为过去四年在GII方面进步最为显著的经济体之一。巴西在政府在线服务(第14位)和电子参与(第11位)等指标上表现出色,均在全球前15位占得一席;16家独角兽公司的估值(第22位)占2023年国内生产总值的1.9%;无形资产(第31位)因其商标(第13位)和全球品牌价值(第39位)而在全球取得良好名次。
Brazil climbs up five ranks this year, firmly establishing itself among the group of economies that have shown the most remarkable improvement in the GII over the past four years. Brazil excels in indicators including government’s online service (at place 14) and e-participation (11), both in the top 15 worldwide; the valuation of its 16 unicorn companies (22), representing 1.9 percent of its GDP in 2023; and intangible assets (31), ranking well worldwide for its trademarks (13), and its global brands value (39).
牙买加(第78位)在创新方面的表现也超出了对发展水平的预期。
Jamaica (78th) also overperforms on innovation for its level of development.
除巴西外,乌拉圭(第63位)和萨尔瓦多(第95位)是该地区今年仅有的排名有所上升的国家。乌拉圭在经商政策(第4位)、信通技术服务进口(第5位)、出口(第7位)以及企业运营稳定性(第10位)方面均位居前十。萨尔瓦多在提供正规培训的公司(第15位)和商标(第20位)方面排名靠前。
In addition to Brazil, Uruguay (63rd) and El Salvador (95th) are the only other countries in the region that have improved their positions this year. Uruguay takes the lead in the top 10 for policies for doing business (4), ICT services imports (5), exports (7), and operational stability for businesses (10). El Salvador stands out with notable rankings in firms offering formal training (15) and trademarks (20).
撒哈拉以南非洲
Sub-Saharan Africa
在撒哈拉以南非洲,毛里求斯(第57位)一马当先,南非(第59位)紧随其后,均进入前60名。其次是博茨瓦纳(第85位)、佛得角(第91位)和塞内加尔(第93位)。该地区有九个经济体的创新排名有所提升。南非、塞内加尔、卢旺达(第103位,在低收入国家中排名第一)、尼日利亚(第109位)、多哥(第114位)和毛里塔尼亚(第127位)等经济体取得了显著进步。
In Sub-Saharan Africa, Mauritius (57th) leads the region, followed by South Africa (59th) making a stride by entering the top 60. Botswana (85th), Cabo Verde (91st) and Senegal (93rd) follow. Nine economies in the region improve their innovation rankings. South Africa, Senegal, Rwanda (103rd, and leading the low-income group), Nigeria (109th), Togo (114th) and Mauritania (127th) are among the economies that have shown notable progress.
毛里求斯在风险资本相对投资额方面居世界首位(第1位),并在接收风险资本方面跻身前五 (第5位)。南非在软件支出(第28位)、本国人专利申请量(第34位)、PCT专利(第40位)和独角兽公司估值(第37位)等指标上表现出色,因此在知识和技术产出方面在本地区拔得头筹。博茨瓦纳在商业成熟度方面遥遥领先,在小额信贷机构贷款方面表现出色(第12位)。
Mauritius leads worldwide in amount of relative VC invested (at place 1) and secures a spot among the top five in VC received (5). South Africa leads the region in knowledge and technology outputs, thanks to its good performance in software spending (28), patents by origin (34), PCT patent applications (40) and valuation of its unicorn companies (37). Botswana leads in business sophistication and performs well in loans from microfinance institutions (12).
塞内加尔在独角兽企业估值方面领先,在资本形成总额(第8位)、小额信贷机构贷款(第10位)、外国直接投资流入量(第13位)和接收的风险资本(第19位)方面表现出色。
Senegal takes the lead for the valuation of its unicorns and it performs well in gross capital formation (8), loans from microfinance institutions (10), FDI inflows (13) and VC received (19).
卢旺达、马达加斯加(第107位)、南非、塞内加尔和布隆迪(第130位)在创新方面的表现均超过对经济发展水平的预期,表现优异,其中卢旺达的表现连续11年可圈可点。
Rwanda, Madagascar (107th), South Africa, Senegal and Burundi (130th) stand out for overperforming on innovation relative to their level of economic development, with Rwanda excelling for 11 years.
“
关于全球创新指数
About the Global Innovation Index
“
2023年全球创新指数(GII)今年是第16版,由产权组织与波图兰研究所合作出版,并得到其企业和学术网络合作伙伴的支持。GII 咨询委员会提供重要指导。
The Global Innovation Index 2023 (GII), in its 16th edition this year, is published by WIPO in partnership with the Portulans Institute, which is supported by its Corporate and Academic Network partners. The GII Advisory Board provides important guidance.
“
视频:2023年全球创新指数
Video: Global Innovation Index 2023
视频:WIPO|Video: WIPO
“
自2007年首次推出以来,GII已打造出衡量创新的议程,并成为了经济决策的基石,越来越多的政府对其年度GII结果展开系统性分析,并制定政策应对措施以改善其表现。
Since its inception in 2007, the GII has shaped the innovation measurement agenda and become a cornerstone of economic policymaking, with an increasing number of governments systematically analyzing their annual GII results and designing policy responses to improve their performance.
GII每年发布,其核心是提供衡量表现的指标并对130多个经济体的创新生态系统进行排名。该指数以丰富的数据集为基础——来自国际公私部门的80个指标集合——超越了传统的创新措施,因为创新的定义已经拓宽。
Published annually, the core of the GII provides performance measures and ranks some 130- plus economies on their innovation ecosystems. The Index is built on a rich dataset – the collection of 80 indicators from international public and private sources – going beyond the traditional measures of innovation since the definition of innovation has broadened.
2023年GII是以两个次级指数的平均值计算的。创新投入次级指数衡量的是支持和促进创新活动的经济要素,这些要素共分为五大类:(1)制度,(2)人力资本与研究,(3)基础设施,(4)市场成熟度和(5)商业成熟度。创新产出次级指数体现的是经济中创新活动的实际成果,分为两大类:(6)知识与技术产出和(7)创意产出。
The GII 2023 is calculated as the average of two sub-indices. The Innovation Input Sub-Index gauges elements of the economy that enable and facilitate innovative activities and is grouped into five pillars: (1) Institutions, (2) Human capital and research, (3) Infrastructure, (4) Market sophistication, and (5) Business sophistication (see Framework). The Innovation Output Sub-Index captures the actual result of innovative activities within the economy and is divided in two pillars: (6) Knowledge and technology outputs and (7) Creative outputs.
每个经济体都有一份创新简报,其中记录了该经济体在所有指标上的表现。这些简报——现在还可以在网上以互动的方式获得——突出了一个经济体在创新方面的相对优势和劣势。
For each economy, an innovation brief is available, in which that economy’s performance on all indicators is recorded. The briefs – now available in an interactive fashion online as well – highlights an economy’s relative innovation strengths and weaknesses.
本指数由欧盟委员会联合研究中心综合指标和记分牌能力中心(COIN)进行独立统计审计。
The index is submitted to an independent statistical audit by the Competence Centre on Composite Indicators and Scoreboards (COIN) from the European Commission’s Joint Research Centre.
“

图:WIPO|Photo: WIPO
点击阅读原文查看关于2023年全球创新指数更多信息。

本篇文章来源于微信公众号: WIPO中国 ,如有侵权请即使联系进行删除








